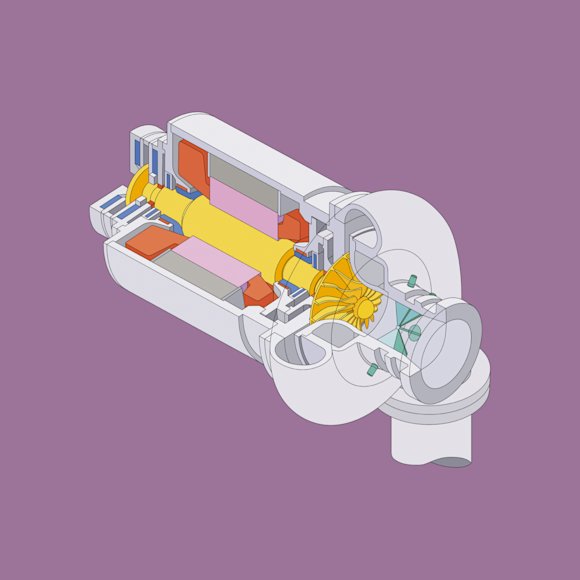
Kawasaki MAG Turbo Single-Stage Sewage Aeration Blower with High-Speed Motor & Magnetic Bearing
Aeration blowers are one of the core facilities for sewage treatment, and these eco-friendly machines contribute to safe, secure, and comfortable lives. No major changes had been made to the basic structure for a long time until the Kawasaki MAG Turbo introduced a technological innovation. The reasons for its high evaluation include the compact size, energy efficiency, and excellent maintainability that requires almost no maintenance.
Numerous Outstanding Features Achieved Through Technological Innovation
Aeration blowers are installed at sewage treatment plants to supply air to biological reaction tanks, where organic matter contained in wastewater is decomposed. Aeration blowers are one of the key facilities in sewage treatment, and they come in various types, including turbo blowers and positive displacement blowers. The existing types of blowers are all mature machinery: no major changes to their basic structure had been made until the Kawasaki MAG Turbo introduced a technological innovation.
After the first MAG Turbo was delivered to a sewage treatment plant in Gifu City, Japan, in 2006, the number of units installed at sewage treatment plants around the country grew steadily and soon reached 130. The MAG Turbo now commands an overwhelming share of single-stage blowers (one impeller). Aota, a senior staff officer at Kawasaki, says, “When customers see the MAG Turbo for the first time, they are truly amazed.”
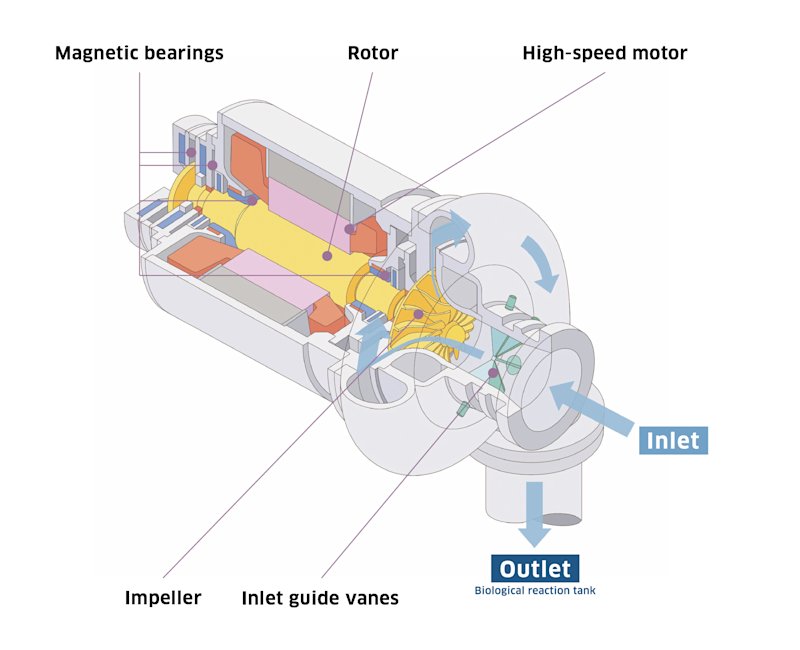
The reasons for the high evaluation include its compact size, energy efficiency, and excellent maintainability requiring almost no maintenance. The high-speed motor featuring magnetic bearings is fitted with an impeller and driven by an inverter.
Unlike conventional-type blowers, the MAG Turbo does not require a lubricant and other auxiliary facilities due to the lack of mechanical contact. It is a compact package, including even the overall control system, and it is optimized as a total system.
One sewage treatment plant has estimated that the MAG Turbo reduced its annual power consumption by approximately 12% compared to its previous blower, which had the same capacity. With the MAG Turbo, it is also possible to install the blower and control equipment separately, offering greater flexibility in installation.
The air volume that a blower is required to provide varies with the season, weather, day of the week, and time of day. To allow for this variation, sewage treatment plants have a number of blowers, including spare units, and they operate different numbers of blowers and adjust the airflow according to the required air volume. The MAG Turbo, which is compact, energy efficient, and easy to maintain, is attracting increasing attention and reputation precisely for this reason.
Although blowers are not high-profile equipment, they bring major benefits by being environmentally friendly and helping make our lives safer and more comfortable.
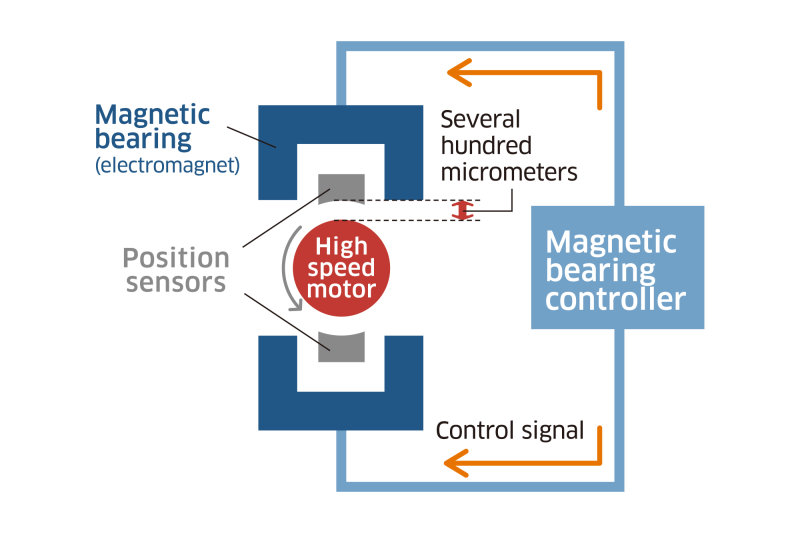
Micron-level Control with Magnetic Bearings
Magnetic bearings levitate the rotor with the magnetic force they exert. The clearance between the rotor and the electromagnets is extremely small. The magnetic bearing controller uses position sensors to accurately determine the rotor’s position relative to the X, Y, and Z axes at all times. The rotor is maintained in its reference position by controlling the amount of electric current provided to the magnetic bearings.
High-speed motor
The high-speed motor contains a rotor that rotates at a high speed. It is integrated with magnetic bearings. The rotation speed is variable via inverter control, which optimizes the speed according to the inlet condition.
Magnetic bearings
Magnetic bearings (electromagnets) are one of the core technologies of the MAG Turbo. The high-speed motor’s rotor is levitated by the magnetic force (the force exerted by the magnets trying to attract the rotor in either direction) of electromagnets. The bearings consist of two radial magnetic bearings and one thrust magnetic bearing. The magnetic bearings minimize mechanical loss, and therefore power consumption is reduced. Since there is no need for a lubricant, related equipment and maintenance are also not required, considerably reducing the maintenance requirement for the overall unit.
It is free from oil leakage since lubrication is not required, it is environmentally friendly, and it is economical since it can go without maintenance for many years!
Low vibration, low noise, and high speed!
Rotor
The rotor is supported by magnetic bearings and has an impeller attached directly to the end of its shaft. It is finished with high precision after being properly heat-treated and is sufficiently durable to withstand long-term use.
Impeller
The impeller is attached to the shaft end of the high-speed motor’s rotor. The impeller is rotated at a high speed as it compresses the air entering through the inlet, then sends the compressed air to the outlet. The design of the impeller’s shape and air channel has always been one of the most advanced technical challenges. In recent years, Kawasaki brought together its aerodynamic technologies and successfully developed a new type of high-efficiency impeller called HYSET, which achieved even greater efficiency.

Inlet guide vanes
Inlet guide vanes efficiently control the air volume by changing their angles in tandem due to the rotation ring, causing the suction airflow to swirl. They are made to withstand long-term use.
Various layout options: a compact design for installation in any space
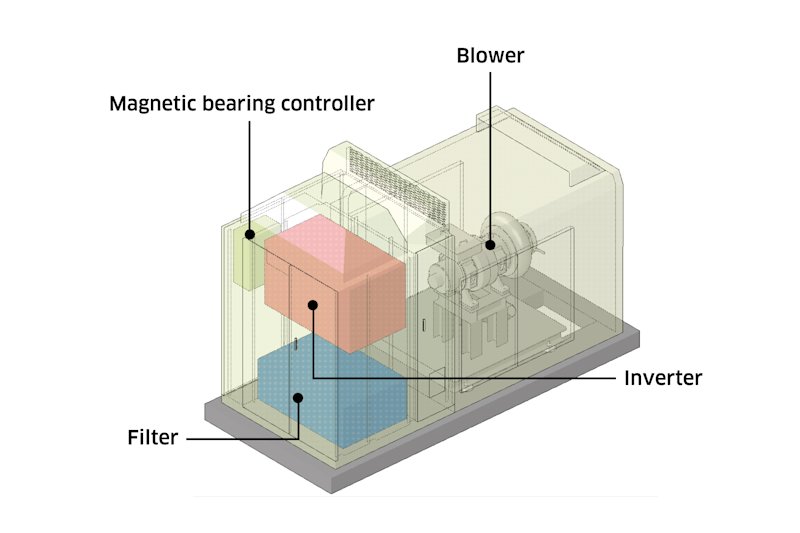
The Kawasaki MAG Turbo consists of a blower, magnetic bearing controller, inverter (alters the frequency and voltage of supplied power to control the rotation speed of the high-speed motor), and other components. Each component is compact and has a small footprint. Another major characteristic is that the blower and control equipment can be installed separately, providing the flexibility to accommodate various installation conditions.

Blower Engineering Section
Aero-Dynamic Machinery Department
Machinery Division
Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.

Blower Engineering Section
Aero-Dynamic Machinery Department
Machinery Division
Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.