Capture CO₂ as you drive! Toyota liquid-hydrogen Corolla in the Super Taikyu race With CO₂ sorbent developed by Kawasaki
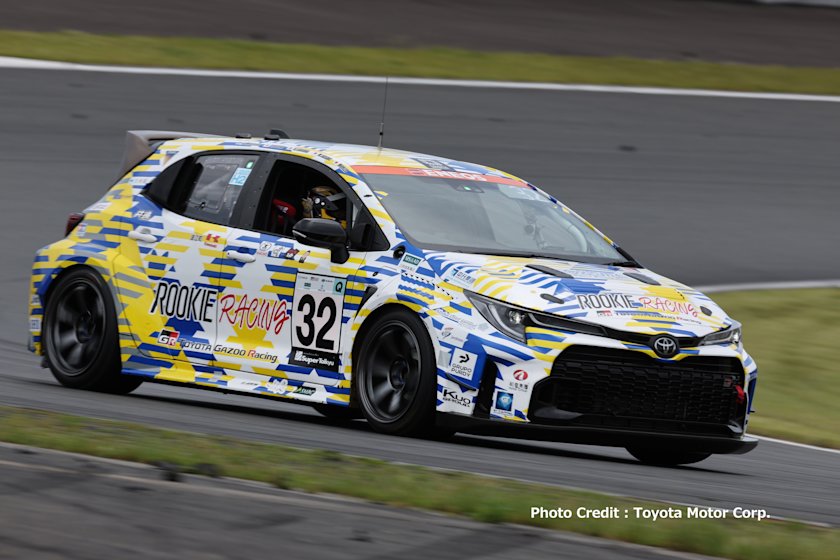

Toyota Motor Corp. announced in 2021 that it was developing a hydrogen engine. Since then, the automaker has been boldly participating in a number of racing competitions with vehicles running on liquid hydrogen. Among such vehicles is the GR Corolla, which has been competing in the Super Taikyu series since 2023. The vehicle, powered by a liquid-hydrogen engine, uses CO₂-absorptive compound (amine) developed by Kawasaki. This article delves into how this compound contributes to Toyota’s carbon-neutral initiatives.
Challenging carbon neutrality in the Super Taikyu race.
Super Taikyu is an endurance racing series featuring commercially available vehicles that have been modified in various ways. Since 2021, Toyota has been participating in the series with hydrogen-powered Corollas as it seeks to advance its carbon-neutral technology.
The 2023 event involved a pilot project by the CO2-free Hydrogen Energy Supply-chain Technology Research Association (HySTRA), of which Kawasaki is a member. In this project, the Corolla was fueled by liquid hydrogen transported from Australia. Subsequently, as Toyota continued to hone its technology, the automaker adopted Kawasaki’s CO2-absorptive compound, which enables the vehicle to capture CO2 in the atmosphere while driving.
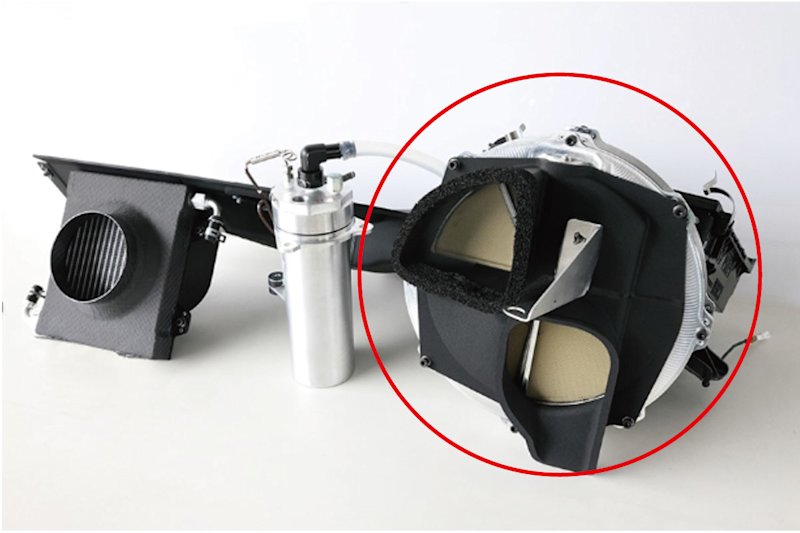

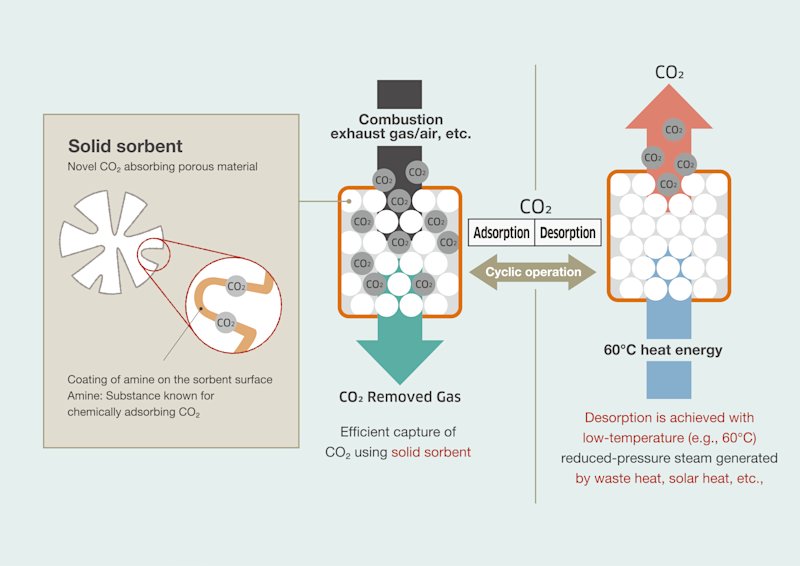
Kawasaki’s CO2 sorbent is applied to the filter of Toyota’s proprietary CO2 capturing system. This CO2 capturing system is located under the hood, next to the engine compartment. The engine draws in air, mixes it with fuel, and creates combustion. The CO2 capturing device installed in the liquid-hydrogen Corolla uses a filter to capture CO2 from the air drawn in, desorbs CO2 using engine heat, and stores highly concentrated CO2 in a small tank.
The CO2 capturing system is undergoing continuous improvements. In the 2023 race, mechanics manually changed the filter during pit stops for repairs and tire changes. For the 2024 race, a new system was developed to automatically rotate the filter. The continuous capturing of CO2 has led to an increase in the capturing rate. The system can now capture 4 grams of CO2 per lap, twice the amount of the previous model. (The length of the Fuji Speedway Racing Course, the venue for the Super Taikyu race, is 4,563 meters.) Kawasaki will continue to contribute to the evolution of Toyota’s CO2 capturing system and further support the realization of carbon neutrality.
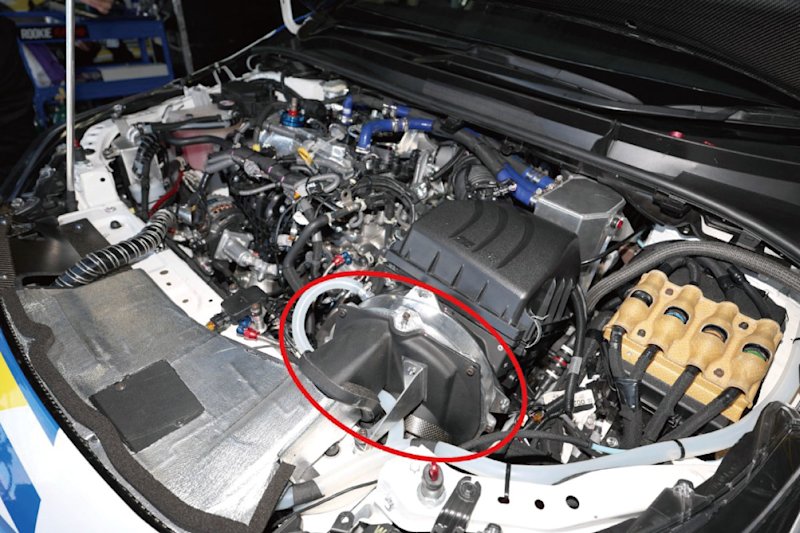

Highly compatible! Kawasaki’s CO2 sorbent x Toyota vehicles
We asked Naoaki Ito, project general manager of the GR Vehicle Development Division at Toyota, why the company adopted Kawasaki’s CO2 sorbent for the liquid-hydrogen Corolla.
“We have been trying to develop a new technology such that the more you drive, the more CO2 you capture. We have adopted Kawasaki’s CO2 sorbent because it allows for CO2 desorption at a low temperature of 60°C. It captures CO2 by using the engine’s air-intake and heat-generation capabilities. We found this feature very appealing. The engine can certainly generate high heat; the temperature exceeds 100°C on a race circuit. However, it does not reach that high on public roads. Therefore, we needed a technology that would enable CO2 desorption at a temperature of less than 100°C. In this way, the more you drive, the more CO2 you capture, even with a regular vehicle. Kawasaki is has that very technology. It allows for CO2 desorption at 60°C. For this reason, there is a very strong affinity between this technology and our vehicles.”
The strength of Kawasaki's CO2 absorbent that can separate CO2 at low temperatures.
Even a vehicle that is said to be fuel-efficient emits about 100 grams of CO2 per kilometer. That is why there are expectations for improving the CO2 capturing rate by adjusting the filter size and rotation speed. “Kawasaki’s CO2-absorptive compound performs very well. Our next challenge is to find a way to store the adsorbed and desorbed CO2 without losing any of it. The GR Vehicle Development Division is making efforts to make ever-better cars through motorsports. We want to develop a car that acts like a CO2 vacuum cleaner, as it were. It will adsorb, desorb, and store CO2 in such a way that the more you drive, the more CO2 you can reduce. We would like to continue to work with you so that we can accomplish this goal and make our vehicles carbon neutral.”
Kawasaki will continue to contribute to Toyota’s efforts to develop carbon-neutral, next-generation vehicles. We will continue to refine our technologies so that we can contribute to the carbon neutrality not only of cars, but also of society as a whole.
Produced with the cooperation of the GR Vehicle Development Division of Toyota Motor Corp.
Interviewee: GR Vehicle Development Division Project General Manager Naoaki Ito
*Departments and titles were current as of the time of the interview.